Introduction to CRM
Overview
CRM is the abbreviation for Customer Relationship Management, a strategy for managing interactions with customers and sales prospects. Most businesses use the term "CRM" to loosely refer to the software system where employees store information about these interactions. Sugar® is one of these systems. Sugar streamlines and automates the business processes that directly and indirectly relate to customers.
Supporting the Customer Lifecycle
A business's overall goals are to find, attract, and win new clients; nurture and retain existing clients; entice former customers back into the fold; and reduce the costs of marketing and customer service. The best CRM systems, like the one developed by SugarCRM, can facilitate interactions throughout this entire customer lifecycle.
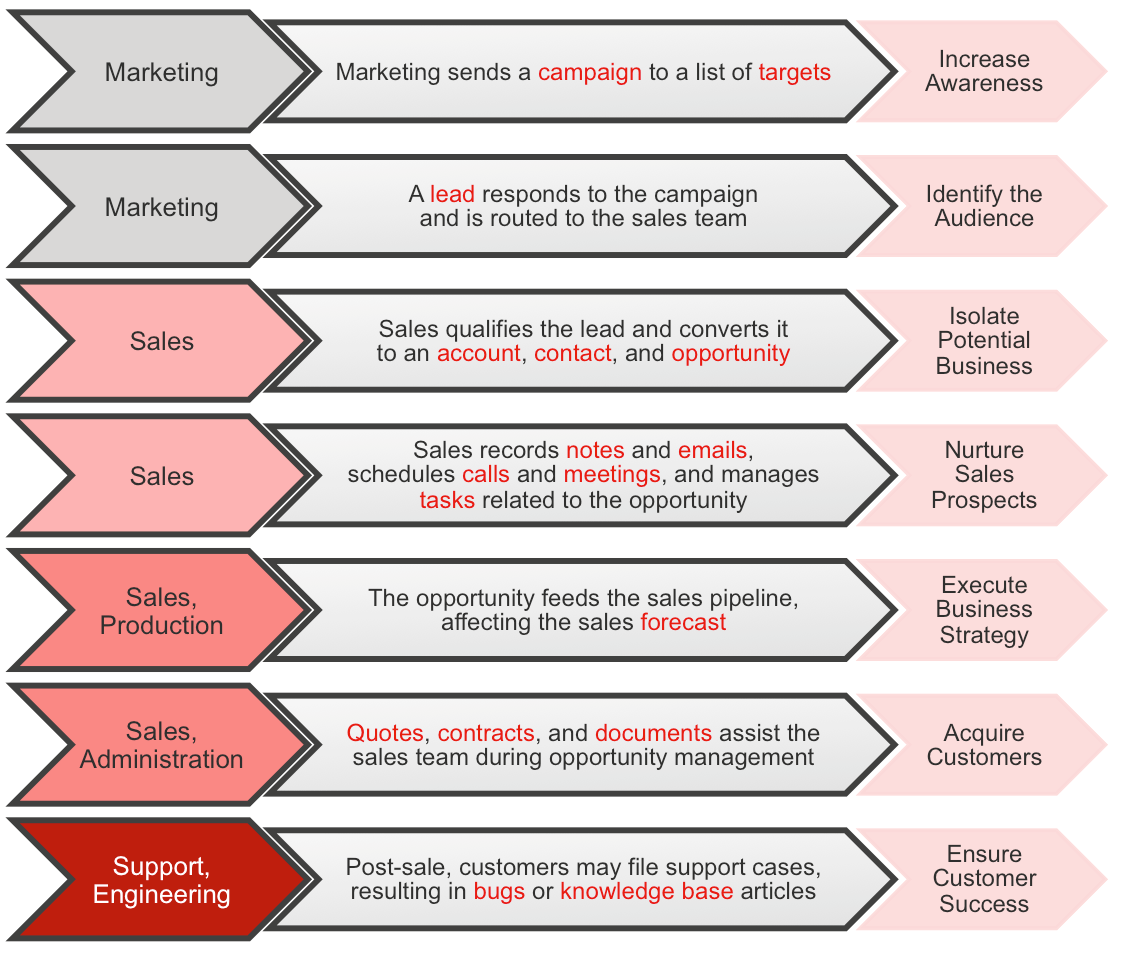
Simply put, the CRM is a place to store interactions with every customer (or potential customer) you talk to. It stores names, addresses, telephone numbers, additional personnel information, emails, calls, meetings, quotes, sales opportunities, support cases and more for all of your customers. Organizations have access to all of the information that affects their relationships with their customers. From introductory conversations to negotiations, from complaints to complaint resolutions, every moment of customer interaction - everything that affects your ability to service the customer and to provide more relevant products or services for them - can (and should!) be captured or recorded in an organization's CRM system.
Use Cases
Sugar's CRM capabilities include (but are definitely not limited to):
- Call Center Management: Sugar's CRM software can be used to set outbound calling schedules and triage incoming calls to the appropriate places.
- Marketing Automation: Marketing teams can plan and execute large-scale campaigns and then perform analytics to determine the most effective programs.
- Sales Force Automation: Streamline the sales process to increase productivity, standardize business processes, and identify key performance indicators.
- Customer Support: Track the questions and concerns that affect existing customers and ensure timely inquiry resolution. Provide feedback to sales and product development teams about common customer issues.
Getting the Most Out of Your CRM System
Data integrity is essential to a perpetual, mutually beneficial relationship between vendors and clients. Train and encourage colleagues to provide information the organization will need to make decisions throughout the customer lifecycle and into the future. Some examples of useful data that are often forgotten include summaries of personal interactions, speculative notes, and even competitive insights.
Tying data together in a logical way is what creates knowledge. Build these data relationships in Sugar by linking contacts, accounts, opportunities, cases, and data from all of the CRM modules together. This will help your business "close the loop" and eliminate detrimental information silos that inhibit the customer experience.