Architecture
Overview
This section of Sugar's Developer Guide begins with a high-level overview of the Sugar platform's architecture and contains documentation on granular concepts in Sugar such as logic hooks, caching, logging, extensions, job queue, and more.
Please continue to the bottom of this page or use the navigation on the left to explore the related content.
Sugar® is built on open standards and technology such as HTML5, PHP, and JavaScript, and runs on a variety of free and open-source technology like Linux, MySQL, and Elasticsearch. The Sugar platform also supports common proprietary databases such as Oracle, IBM DB2, and Microsoft SQL Server.
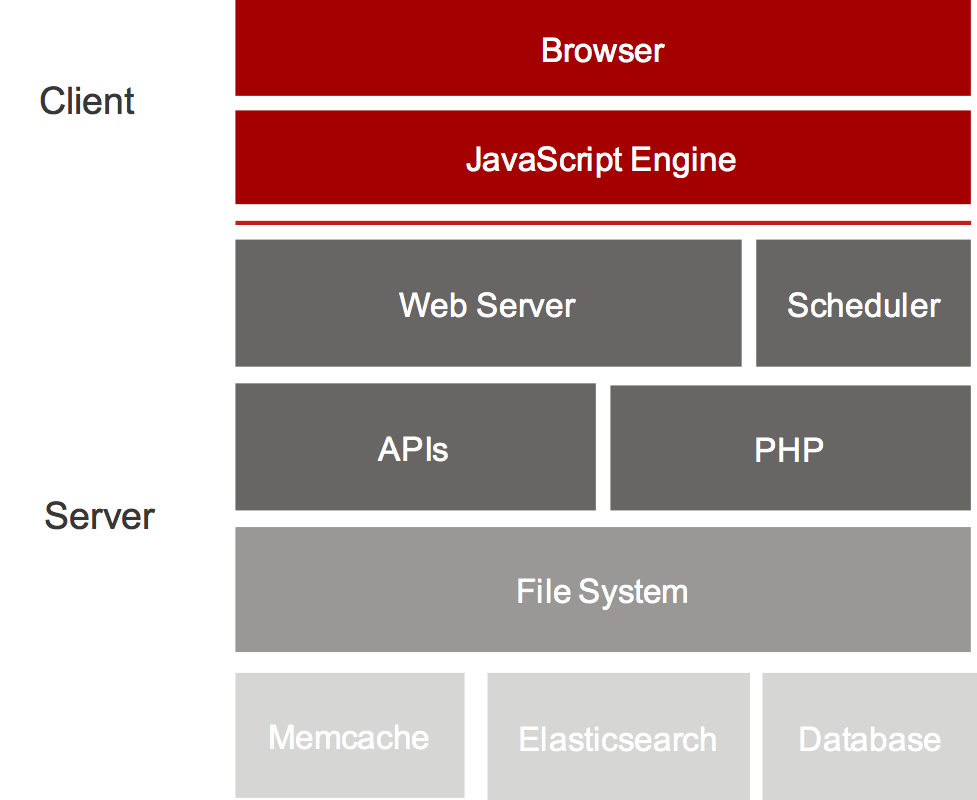
All of Sugar's customers and partners have access to source code that they can choose to deploy on-premise or utilize Sugar's cloud service for a SaaS deployment.
Out of the box, Sugar uses a consistent platform across all clients and devices (e.g. mobile, web, plug-ins, etc.).
Front-End Framework
Our clients are based on a front-end framework called Sidecar. Sidecar is built on open source technology: Backbone.js, jQuery, Handlebars.js, and Bootstrap. The Sidecar framework provides a responsive UI (to support a variety of form factors) and uses modern, single-page client architecture. Sugar clients connect to Sugar server application via our client REST API. The REST API is implemented in PHP and drives server-side business logic and interacts with a database. If it can be accomplished via one of our clients, then its equivalent functionality can be accomplished using our REST API.
The Sugar platform uses modules. Modules are a vertically integrated application component that is traditionally organized around a single feature or record type (or underlying database table). For example, contact records are managed via a Contacts module that contains all the business logic, front-end interface definitions, REST APIs, data schema, and relationships with other modules.
Custom modules can be created and deployed as needed in order to add new features to a Sugar application instance.
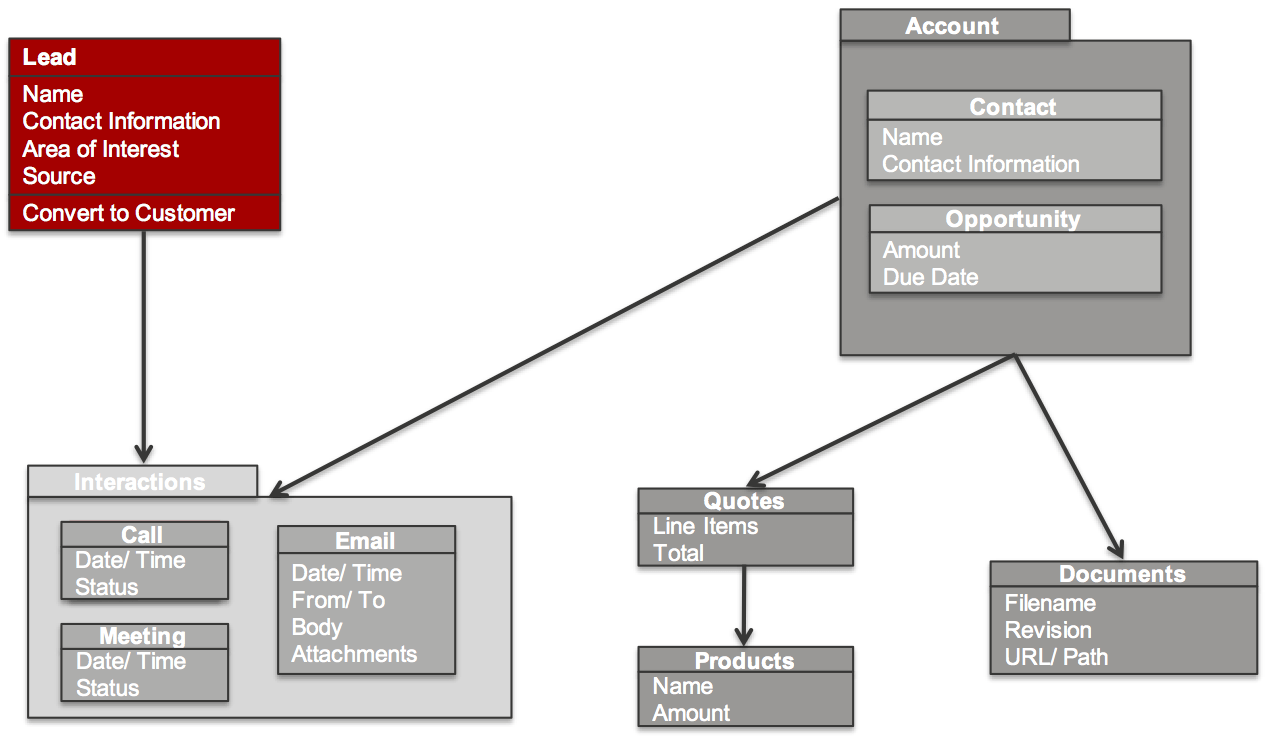
Sugar's modules are defined primarily using Metadata. There are two types of metadata definitions within Sugar: Vardefs, which define the data model for Sugar modules; and Viewdefs, which define the user interface components that are used with a module.
Sugar Metadata is implemented as PHP files that can be modified directly by a Sugar Developer making filesystem changes, or indirectly through the use of Sugar Studio and Module Builder by a Sugar Administrator.
Metadata allows you to configure solutions instead of having to write countless lines of custom code in order to implement common customizations such as adding custom fields, calculated values, and changing user interface layouts.
Extensions
Beyond metadata, Sugar is highly customizable and includes an extensive Extensions Framework that provides Sugar Developers the capability to contribute to pre-defined extension points within the application in a way that is upgrade-safe and will not conflict with other customizations that exist in the system.
Topics
The autoloader is an API that allows the unified handling of customizations and customizable metadata while reducing the number of filesystem accesses and improving performance.
Much of Sugar's user interface is built dynamically using a combination of templates, metadata and language files. A file caching mechanism improves the performance of the system by reducing the number of static metadata and language files that need to be resolved at runtime. This cache directory stores the compiled files for JavaScript files, Handlebars templates, and language files.
The upload directory is used to store files uploaded for imports, attachments, documents, and module loadable packages.
Outlines the relationships between emails, email addresses, and bean records.
Recommended approaches when working with email addresses in Sugar.
There are two logging systems implemented in the Sugar application: SugarLogger and PSR-3. PSR-3 is Sugar's preferred logger solution and should be used going forward.
The Logic Hook framework allows you to append actions to system events such as when creating, editing, and deleting records.
Sugar as an application platform is internationalized and localizable. Data is stored and presented in the UTF-8 codepage, allowing for all character sets to be used. Sugar provides a language-pack framework that allows developers to build support for any language in the display of user interface labels. Each language pack has its own set of display strings which is the basis of language localization. You can add or modify languages using the information in this guide.
The extension framework, defined in ./ModuleInstall/extensions.php, provides the capability to modify Sugar metadata such as vardefs and layouts in a safe way that supports installing, uninstalling, enabling, and disabling without interfering with other customizations.
Filters are a way to predefine searches on views that render a list of records such as list views, pop-up searches, and lookups. This page explains how to implement the various types of filters for record list views.
The duplicate-check framework provides the capability to alter how the system searches for duplicate records in the database when creating records. For information on duplicate checking during imports, please refer to the index documentation.
The focus of this document is to guide developers on how Sugar integrates with Elastic Search.
How to customize the global search results.
Sugar Logic, a feature in all Sugar products, enables custom business logic that is easy to create, manage, and reuse on both the server and client.
The Administration class is used to manage settings stored in the database config table.
The Configurator class, located in ./modules/Configurator/Configurator.php, handles the config settings found in ./config.php and ./config_override.php.
Module Loader is used when installing customizations, plugins,language packs, and hotfixes, and other customizations into a Sugar instance in the form of a Module Loadable Package. This documentation covers the basics and best practices for creating module loadable packages for a Sugar installation.
The Module Builder tool allows programmers to create custom modules without writing code and to create relationships between new and existing CRM modules. To illustrate how to use Module Builder, this article will show how to create and deploy a custom module.
As of Sugar 7.9.0.0, the quotes module has been moved out of Backward Compatibility mode into Sidecar. Customizations to the Quotes interface will need to be rewritten for the new Sidecar framework as an automated migration of these customizations is not possible. This document will outline common customizations and implementation methods.
SugarBPM™ automation suite is the next-generation workflow management tool for Sugar. Introduced in 7.6, SugarBPM is loosely based on BPMN process notation standards and provides a simple drag-and-drop user interface along with an intelligent flow designer to allow for the creation of easy yet powerful process definitions.
Entry points, defined in ./include/MVC/Controller/entry_point_registry.php, were used to ensure that proper security and authentication steps are applied consistently across the entire application. While they are still used in some areas of Sugar, any developers using custom entry points should adjust their customizations to use the latest REST API endpoints instead.
The Job Queue executes automated tasks in Sugar through a scheduler, which integrates with external UNIX systems and Windows systems to run jobs that are scheduled through those systems. Jobs are the individual runs of the specified function from a scheduler.
Access Control Lists (ACLs) are used to control access to the modules, data, and actions available to users in Sugar. By default, Sugar comes with a default ACL Strategy that is configurable by an Admin through the Roles module via Admin > Role Management. Sugar also comes with other ACL strategies that are located in the ./data/acl/ folder, and are used in other parts of the system such as the Administration module, Emails module, Locked Fields functionality, and many others. They can also be leveraged by customizations and custom ACL strategies can be implemented to control your own customizations.
Teams provide the ability to limit access at the record level, allowing sharing flexibility across functional groups. Developers can manipulate teams programmatically provided they understand Sugar's visibility framework.
The tagging feature allows a user to apply as many "tags" as they choose on any record they want to categorize. This allows the user to effectively group records together from any source within the application and relate them together. Please note that the tag field and Tags module do not support customization at this time.
This section contains information about working with the TinyMCE editor in Sugar.
This section contains information on generating PDFs and configuring PDF settings and fonts in Sugar.
The SugarDateTime class, located in, ./include/SugarDateTime.php, extends PHP's built in DateTime class and can be used to perform common operations on date and time values.
Shortcuts is a framework to add shortcut keys to the application. When shortcut keys are registered, they are registered to a particular shortcut session. Shortcut sessions group shortcut keys, and they can be activated, deactivated, saved, and restored. Global shortcut keys can be registered, but they are not tied to a particular shortcut session. They are rather applied everywhere in the application and can only be applied once.
How to customize the Sugar theme.
Learn about the Sugar Accessibility Plugin for Sidecar.
This article will cover how to add validation constraints to your custom code.
Sugar on-premise deployments include a command line interface tool built using the Symfony Console Framework. Sugar's CLI is intended to be an administrator or developer level power tool to execute PHP code in the context of Sugar's code base. These commands are version specific and can be executed on a preinstalled Sugar instance or on an installed Sugar instance. Sugar's CLI is not intended to be used as a tool to interact remotely with an instance nor is it designed to interact with multiple instances.
The Performance Tuning section contains information that will help maximize system performance for your Sugar instance.
As of Sugar® 7, modules are built using the Sidecar framework. Any modules that still use the MVC architecture and have not yet migrated to the Sidecar framework are set in what Sugar refers to as "backward compatibility" (BWC) mode.


