SugarBPM
Introduction
SugarBPM™ automation suite is the next-generation workflow management tool for Sugar. Introduced in 7.6, SugarBPM is loosely based on BPMN process notation standards and provides a simple drag-and-drop user interface along with an intelligent flow designer to allow for the creation of easy yet powerful process definitions.
Note: SugarBPM™ is not available for Sugar Professional.
SugarBPM enables administrators to streamline common business processes by managing approvals, sales processes, call triaging, and more. The easy-to-use workflow tool adds advanced BPM functionality to the core Sugar software stack.
A business process is a set of logically related tasks that are performed in order to achieve a specific organizational goal. It presents all of the tasks that must be completed in a simplified and streamlined format. SugarBPM empowers Sugar administrators, allowing for the automation of vital business processes for their organization. The SugarBPM automation suite features an extensive toolbox of modules that provide the ability to easily create digital forms and map out fully functioning workflows.
SugarBPM Modules
SugarBPM is broken down into four distinct modules, each with its own area of responsibility. Three of the four SugarBPM modules have access control settings that restrict its visibility to System Administrators, Module Administrators, and Module Developers.
Process Definitions
A process definition defines the steps in an overall business process. Process definitions are created by either a Sugar administrator, a module Administrator or a module Developer. The process definition consists of a collection of activities and their relationships, criteria to indicate the start and end of the process, and information about the individual activities (e.g., participants) contained within the business process.
Business Rules
A business rule is a reusable set of conditions and outcomes that can be embedded in a process definition. The set of rules may enforce business policy, make a decision, or infer new data from existing data. For example, if Sally manages all business opportunities of $10,000 or more, and Chris manages all business opportunities under $10,000, a business rule can be created and used by all relevant process definitions based on the same target module to ensure that the assignment policy is respected. In the case of an eventual personnel change, only the business rule will need to be edited to affect all related processes.
Email Templates
A process email template is required in order to include a Send Message event in a process definition. The SugarCRM core product includes several places where email templates can be created for different purposes, but SugarBPM requires all sent messages to be created via the Process Email Templates module.
Processes
A process is a running instance of a process definition. A single process begins every time a process definition meeting certain criteria is executed. For example, a single process definition could be created to automate quote approvals, but because users may engage in several quote approvals per day, each approval will be represented by a separate process instance, all governed by the single process definition.
Database Tables
Information surrounding various portions of SugarBPM can be found in the following SugarBPM database tables:
| Table name | Description |
|---|---|
| pmse_bpm_access_management | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpm_activity_definition | Holds definition data for an activity. Maps directly to the pmse_bpmn_activity table and may, in the future, be merged with the pmse_bpmn_activity table to prevent forked data backends. |
| pmse_bpm_activity_step | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpm_activity_user | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpm_config | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpm_dynamic_forms | Holds module specific form information - basically viewdefs for a module - for a process. |
| pmse_bpm_event_definition | Holds definition data for an event. Maps directly to the pmse_bpmn_event table and may, in the future, be merged with the pmse_bpmn_event table to prevent forked data backends. |
| pmse_bpm_flow | Holds information about triggered process flows as well as state of any process that is currently running. |
| pmse_bpm_form_action | Holds information about a process that has been acted upon. |
| pmse_bpm_gateway_definition | Holds definition data for a gateway. Maps directly to the pmse_bpmn_event table and may, in the future, be merged with the pmse_bpmn_gateway table to prevent forked data backends. |
| pmse_bpm_group | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpm_group_user | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpm_notes | Holds notes saved for a process record. |
| pmse_bpm_process_definition | Holds definition data for a process definition. Maps directly to the pmse_bpmn_process table and may, in the future, be merged with the pmse_bpmn_process table to prevent forked data backends. |
| pmse_bpm_related_dependency | Holds information about dependencies related to an event |
| pmse_bpm_thread | Holds information related to process threads for running processes. |
| pmse_bpmn_activity | Please see pmse_bpm_activity_definition |
| pmse_bpmn_artifact | Holds BPM artifact information, like Comments on a process diagram. At present, SugarBPM only supports the text annotation artifact. |
| pmse_bpmn_bound | Data related to element boundaries on the diagram. |
| pmse_bpmn_data | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpmn_diagram | Data related to a process definition's diagram. |
| pmse_bpmn_documentation | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpmn_event | Please see pmse_bpm_event_definition |
| pmse_bpmn_extension | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpmn_flow | Holds information about the connecting flows of a diagram. |
| pmse_bpmn_gateway | Please see pmse_bpm_gateway_definition |
| pmse_bpmn_lane | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpmn_laneset | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpmn_participant | This table is not used. |
| pmse_bpmn_process | Please see pmse_bpm_process_definition |
| pmse_business_rules | Holds business rule record data. |
| pmse_emails_templates | Holds email template record data. |
| pmse_inbox | Holds information about processes that are currently running or that have completed. |
| pmse_project | Holds process definition record information. |
Relationships
The following Entity Relationship Diagram highlights the relationships between the various SugarBPM tables.
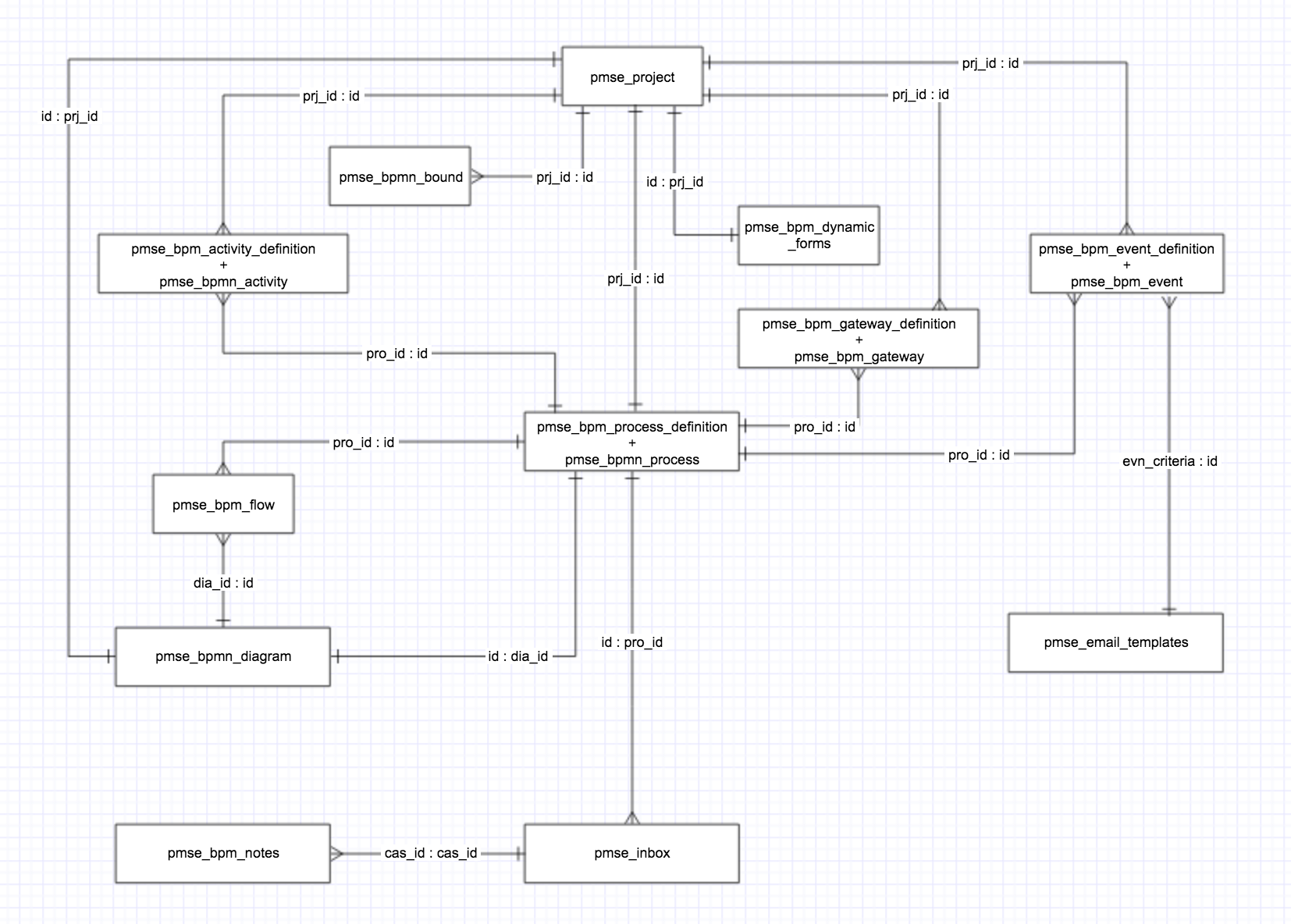
Flows
When a process definition is created the following 5 tables get populated:
pmse_bpm_dynamic_formscontainsdyn_view_defswhich is the JSON encoded string of module-specific form informationpmse_bpm_process_definitioncontains the module associated with and the status of a process definitionpmse_bpmn_diagramcontains process definition name as well and a diagram uidpmse_bpmn_processcontains process definition name. The same Id is shared between pmse_bpm_process_definition and pmse_bpmn_process dia_id is a foreign key related to pmse_bpmn_diagrampmse_projectcontains process definition name, project id, module, status. Other tables have a foreign key of prj_id in them.
Upon adding a start/end/send message event:
pmse_bpmn_eventcontains event namepmse_bpm_event_definitionShares id with pmse_bpmn_eventpmse_bpmn_bound
When Settings is changed to "New Records Only"
pmse_bpm_related_dependency
Upon adding an action or activity:
pmse_bpm_activity_definitioncontains the action name- The
act_fieldscolumn contains the JSON encoded list of fields which will be changed
- The
pmse_bpm_activitycontains action name. Shares id withpmse_bpm_activity_definition.act_script_typecontains the type of action e.g. CHANGE_FIELDpmse_bpmn_bound
Upon adding a connector between start event and action:
pmse_bpmn_flowcontains origin and destination info
Upon adding a Gateway:
pmse_bpm_gateway_definitionpmse_bpm_gatewayshares id withpmse_bpm_gateway_definitionpmse_bpmn_flowflo_conditioncontains JSON encoded string of conditions required to proceed ahead with an action or activitypmse_bpmn_bound
When a process runs:
pmse_inboxcas_statusindicates the status of a processpmse_bpm_threadpmse_bpm_flowStores the entire flow that the process elements went through (so if 3 elements and 2 connectors are in the process definition then 5 records will exist)
After Process has run and appears in Process Management:
pmse_bpm_case_datapmse_bpm_form_actioncontainsfrm_action,cas_pre_data, andcas_data
Add a comment:
pmse_bpmn_artifactcontains the commentpmse_bpm_bound
Add a business rule to a process definition:
pmse_business_rulesrst_source_definitioncontains the conditions of the business rulepmse_bpm_activity_definitionact_fieldscontains the business rule id
Add an email template to a process definition:
pmse_email_templatespmse_bpm_event_definitionevn_criteriacontains the email template id
Extension and Customization
In Sugar 7.8, Sugar introduced the Process Manager library to support extending SugarBPM in an upgrade-safe way. For more information on extending SugarBPM, or on using the Process Manager library, please read the Process Manager documentation.
Caveats
In Sugar 7.8, the Process Manager library brought Registry Object to maintain the state of SugarBPM processes during a PHP Process. This change introduced a limitation in SugarBPM that prevents the same process definition from running on multiple records inside the same PHP process. For certain customizations in Sugar, if you are updating multiple records in a module using SugarBean, you may want them to trigger the defined process definitions for each record.
The following code can be added to your customization to allow for that functionality:
use Sugarcrm\Sugarcrm\ProcessManager\Registry;
//custom code
Registry\Registry::getInstance()->drop('triggered_starts');
$bean->save();
The 'triggered_starts' registry contains the Start Event IDs that have been triggered previously in the PHP process, thus allowing the SugarBean::save() method to trigger SugarBPM and go through the same Start Event again.